Example: Connecting the Dots
- a key goal of the Semantic Web is to aid in combining information
(statements) about specific instances from multiple sources
- RDF and DAML provide several mechanisms to accomplish this
- the following examples use the family of President George W. Bush,
using fictitious email addresses as URIs
- RDF implicitly collects statements about the same URI, e.g.
given the inputs
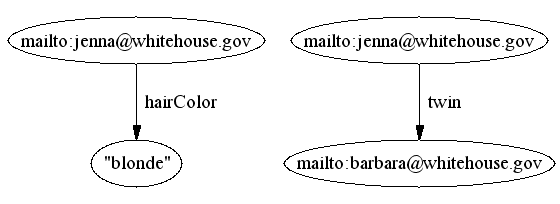
we get
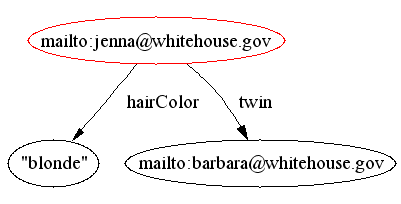
- RDF includes a concept of blank (anonymous) nodes that allow us to
refer to things by description, e.g.
Blank nodes can be merged.
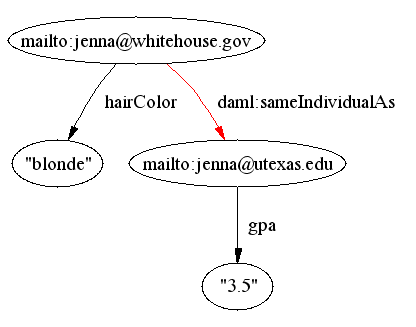
- daml:sameIndividualAs
allows us to explicitly link different URIs for the same instance,
e.g.
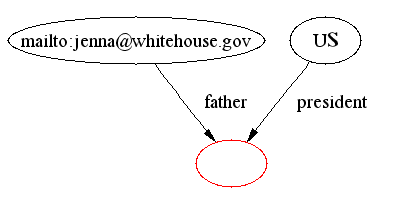
- DAML ontology cardinality constraints
(particularly cardinality 1) can allow us to infer equivalence,
e.g. a Person has only 1 father so
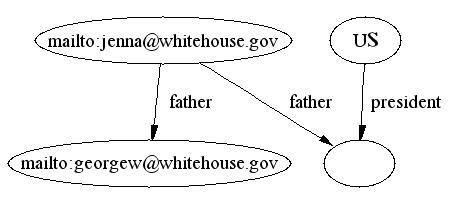
implies
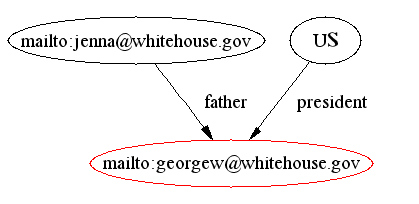
- daml:UnambiguousProperty
can allow us to merge nodes based on a property value,
e.g. if emailAddress is unambiguous, then
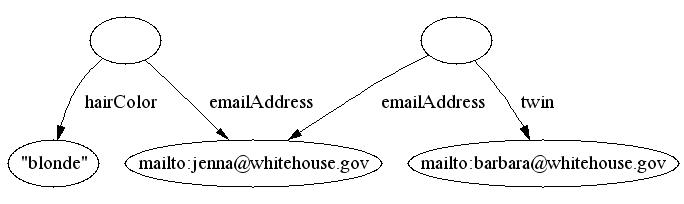
implies
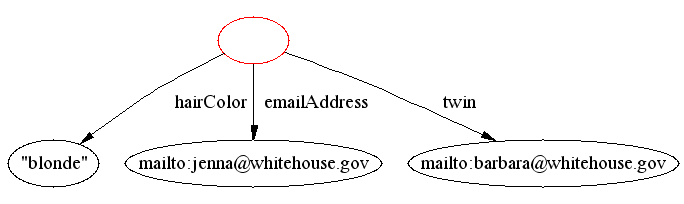
- some inferences can't currently be expressed using DAML+OIL
due to their computational complexity exceeding the tractability
threshold of
Description Logics,
e.g. from
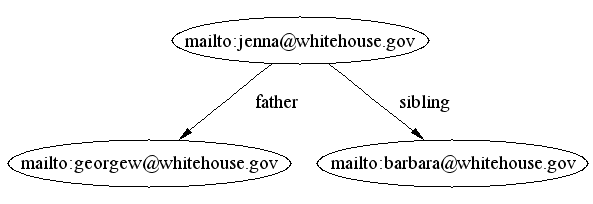
we might expect to infer
but we can't currently.
DAML Rules
will be able to express such
inference rules, translation rules, etc.
- DAML Proof
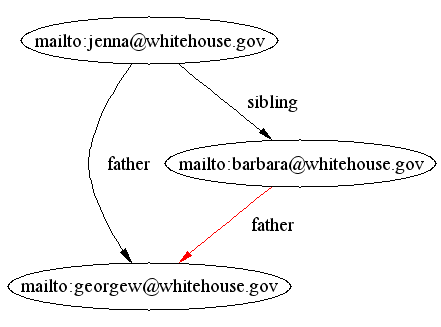
will trace the inferences made, e.g.
given
we might conclude

with a proof like
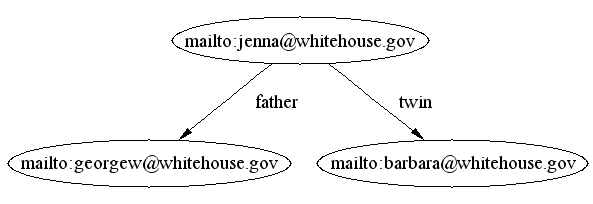
- jenna sibling barbara
because
twin daml:subPropertyOf sibling
- barbara father georgew
because of the DAML Rules rule discussed above













